In this post, we are going to learn to Send Emails with NodeJS and NodeMailer library. Email is one of the commonly used tools for communication in web applications because it helps us to reach your users instantly, build your business and promotions, or send endless notifications.
There are several Node.js modules used for sending emails. In that, nodemailer is the most familiar option. This package has a module that gives you the ability to quickly send emails without bother. The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is used for sending email between servers.
Step 1: Install nodeJs package and Init application
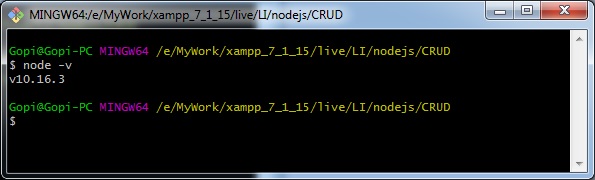
Initially download NodeJS and install it in your system and confirm everything configured correctly using the following command.
|
1 |
node -v |
Step 2: Create a directory and init application
Create an application folder and init the project using the following command.
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
mkdir email_nodejs cd email_nodejs npm init --yes |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
{ "name": "email_nodejs", "version": "1.0.0", "description": "", "main": "index.js", "scripts": { "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1" }, "keywords": [], "author": "", "license": "ISC", "dependencies": { "body-parser": "^1.19.0", "ejs": "^3.0.1", "express": "^4.17.1", "nodemailer": "^6.4.2" } } |
Step 3: Install required packages using NPM
The following modules are going to be required to create the application.
- Express: Express is a least and adjustable Node.js web application framework that gives a strong collection of features for web and mobile applications. Express gives a light layer of basic web application benefits, without covering Node.js benefits that you agree and like.
- body-parser: used to parse incoming requests from the end client.
- ejs: is a templating engine and its used to render HTML pages to end client
- NodeMailer: There are several Node.js modules used for sending emails. In that, nodemailer is the most familiar option. This package has a module that gives you the ability to quickly send emails without bother.
- nodemon: Optional package and Installed globally. It helps us to listen for modifications to files and automatically restart the app server.
Run the following command to install the above mention modules as dependencies for our application.
|
1 2 |
npm install --save express nodemailer body-parser ejs npm install -g nodemon (optional - used to run app.js automatically while any file content changes) |
Step 4: Create app.js file
Create app.js server file and include the required dependency package in it for our file upload application. And define the server port and write an app server .listen() function.
Create app.js file
|
1 |
touch app.js |
include following code
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
const path = require('path'); const express = require('express'); const ejs = require('ejs'); const bodyParser = require('body-parser'); const app = express(); // Server Listening app.listen(3000, () => { console.log('Server is running at port 3000'); }); |
Run app.js using following comment
|
1 |
nodemon app (OR) npm start |
Step 5: Define View engine with ejs / public path / View files path
Here we are going to define a template view engine with ejs using set() and use() function and also define a Public path and View folder path location.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
//set views file app.set('views',path.join(__dirname,'views')); //set view engine app.set('view engine', 'ejs'); app.use(bodyParser.json()); app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false })); |
Step 6: Define and configure ModeMailler and transporter details
We need to include the NodeMailer package into our app.js and define a service provider to send mail to various servers. NodeMailer requires a transport service utilizing which it can send emails. In this article, we are using the Gmail service to sent mail to various client servers. For defining transposer services we need to add the following code into the app.js file.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
.... .... const nodemailer = require('nodemailer'); .... .... let transporter = nodemailer.createTransport({ host: 'smtp.googlemail.com', port: 465, auth: { pass: 'xxxxxxxxxxxx' }, tls: { rejectUnauthorized: false } }); .... .... |
Step 7: Define index path with ‘/’ and HTML file
Here we are going to define the HTML page with ejs extension and adding HTML content in it. We created four HTML files for file upload operation. I am going to create a file with named as email.js
Index route Request handler
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
// Base index route app.get('/',(req, res) => { res.render('email', { title: 'Send Emails with NodeJS and Express' }); }); |
For Email From
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 |
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <title><%= title %></title> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.3.1/css/bootstrap.min.css"> <script src="https://ajax.googleapis.com/ajax/libs/jquery/3.4.1/jquery.min.js"></script> <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/popper.js/1.14.7/umd/popper.min.js"></script> <script src="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.3.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script> <style> body { background: #f1eded; } .title { margin: 10px; background: #e07214; color: #fff; padding: 15px 0px; border-radius: 5px; border-bottom: solid 7px #90531e; } .app-form { background: #fff; padding: 2% 3%; border-radius: 5px; border: solid 1px #e07214; } .app-form input, .app-form textarea { border: solid 1px #0a5b8a; } .app-form label { color: #0a5b8a; font-weight: 600; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="container"> <h2 class="text-center title"><%= title %></h2> <div class="row"> <div class="offset-md-3 col-md-6 app-form"> <form action="/sendmail" method="POST" autocomplete="off"> <div class="form-group"> <label for="to_email">To E-Mail:</label> <input type="email" class="form-control" name="to_email" id="to_email" required> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="mail_subject">Subject:</label> <input type="text" class="form-control" name="mail_subject" id="mail_subject" required> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="message">Message:</label> <textarea type="textarea" class="form-control" name="message" id="message" required></textarea> </div> <div class="checkbox"> <label><input type="checkbox" name="attach" value="1"> With Promotion Attachment</label> </div> <button type="submit" name="send_mail" class="btn btn-primary">Send Mail</button> </form> </div> </div> <br/> <br/> </div> </body> </html> |
Step 8: Define Email form post function handler in app.js
Here we are going to define the email form handling and sending email functions using NodeMailer.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 |
.... .... app.post('/sendmail',(req, res) => { let to_email = req.body.to_email; let mail_subject = req.body.mail_subject; let message = req.body.message; let messageOptions = { to: to_email, subject: mail_subject, text: message }; transporter.sendMail(messageOptions, (error, info) => { if (error) { return console.log(error); } console.log('Message %s sent: %s', info.messageId, info.response); res.redirect('/'); }); }); .... .... |
For sending HTML content in EMail,
We can able to sent Email with HTML content using “html” attribute. Instead of “text” attribute we can replace with “html” for this option.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
.... .... let messageOptions = { to: to_email, subject: mail_subject, html: message }; .... .... |
For sending HTML content with Attachment in EMail,
We can able to sent Email with Attachments using “attachments” attribute. Attachments attribute have two arguments for file attachments. It have filename and path for file attachments.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
.... .... attachments: [{ filename: 'File Name', path: 'File Full Path' }] .... .... |
Final and full Mail function setup for sending emails,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
.... .... app.post('/sendmail',(req, res) => { let to_email = req.body.to_email; let mail_subject = req.body.mail_subject; let message = req.body.message; let attach = req.body.attach; let messageOptions = { to: to_email, subject: mail_subject, // text: message html: message }; if(attach){ messageOptions = {...messageOptions, attachments: [{ filename: 'Promotion.jpg', path: './Promotion.jpg' }] }; } transporter.sendMail(messageOptions, (error, info) => { if (error) { return console.log(error); } console.log('Message %s sent: %s', info.messageId, info.response); res.redirect('/'); }); }); .... .... |
Step 9: Run a server and check with Browser
Here we are going to run an application with the following command to test our Send Emails with NodeJS and NodeMailer application in a browser.
Finally app.js file code following details.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 |
const path = require('path'); const express = require('express'); const ejs = require('ejs'); const bodyParser = require('body-parser'); const nodemailer = require('nodemailer'); const app = express(); //set views file app.set('views',path.join(__dirname,'views')); //set view engine app.set('view engine', 'ejs'); app.use(bodyParser.json()); app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false })); let transporter = nodemailer.createTransport({ host: 'smtp.googlemail.com', port: 465, auth: { pass: 'learninfinity#2017' }, tls: { rejectUnauthorized: false } }); // Base index route app.get('/',(req, res) => { res.render('email', { title: 'Send Emails with NodeJS and Express' }); }); app.post('/sendmail',(req, res) => { let to_email = req.body.to_email; let mail_subject = req.body.mail_subject; let message = req.body.message; let attach = req.body.attach; let messageOptions = { to: to_email, subject: mail_subject, // text: message html: message }; if(attach){ messageOptions = {...messageOptions, attachments: [{ filename: 'Promotion.jpg', path: './Promotion.jpg' }] }; } transporter.sendMail(messageOptions, (error, info) => { if (error) { return console.log(error); } console.log('Message %s sent: %s', info.messageId, info.response); res.redirect('/'); }); }); // Server Listening app.listen(3000, () => { console.log('Server is running at port 3000'); }); |
Run the Application using the following command.
|
1 2 3 |
npm start (OR) nodemon app http://localhost:3000/ |
Now you are ready to see the demonstration of Send Emails with NodeJS and NodeMailer.
Download